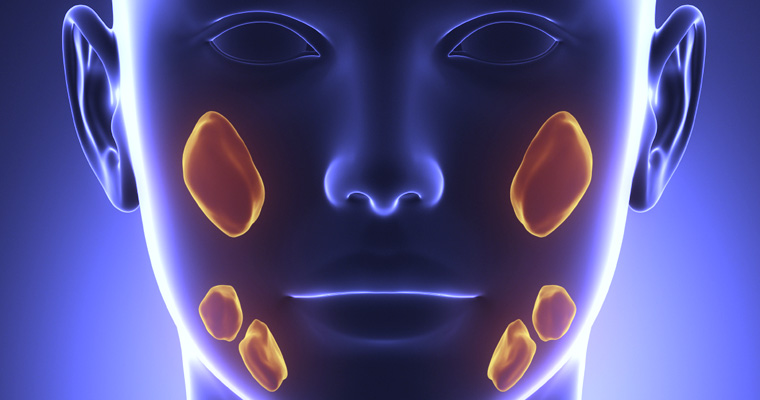
Surgery to remove all or part of the parotid gland (a large salivary gland located in front of and just below the ear). In a radical parotidectomy, the entire gland is removed.
General information about Parotidectomy.
The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands. There are two parotid glands, one on each side of the face. They lie just in front of the ears and a duct runs from each to the inside of the cheek. Each parotid gland has several lobes. Surgery is recommended as part of the treatment for all cancers in the parotid gland. Superficial or localized parotidectomy is recommended by some authorities, unless a lipoma or Warthin’s tumor is present. One of the advantages to this approach is that nerves to facial muscles are left intact. Many facial nerves run through the same area as the parotid gland and can be damaged during more complete parotidectomies. Most authorities recommend total parotidectomy, especially if cancer is found in both the superficial and deep lobes of the parotid gland. If the tumor has spread to involve the facial nerve, the operation is expanded to include parts of bone behind the ear (mastoid) to remove as much tumor as possible. Some authorities recommend post-surgery radiation as follow-up treatment for cancer.
Why a Parotidectomy is performed?
The main purpose of parotidectomy is to remove cancerous tumors in the parotid gland. A number of tumors can develop in the parotid gland. Many of these are tumors that have spread from other areas of the body, entering the parotid gland by way of the lymphatic system. Among the tumors seen in the parotid gland are lymphoma, melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Risks associated with Parotidectomy
There are a number of complications that follow parotidectomy. Facial nerve paralysis after minor surgery should be minimal. During surgery, it is possible to repair cut nerves. After major surgery, a graft is attempted to restore nerve function to facial muscles. Salivary fistulas can occur when saliva collects in the incision site or drains through the incision. Reoccurrence of cancer is the single most important consideration for patients who have undergone parotidectomy. Long term survival rates are largely dependent on the tumor types and the stage of tumor development at the time of the operation.
Other risks include blood clots (hematoma) and infection. The most common long-term complication of parotidectomy is redness and sweating in the cheek, known as Frey’s syndrome. Rarely, paralysis may extend throughout all the branches of the facial nervous system.